Industrial robots are fully automated machines composed of a manipulator and a control system. Before starting their operation, robots are programmed by setting parameters required for specific tasks, including movement along a trajectory and manipulation of the robotic arms.
The movement of industrial robots within buildings and structures can occur through the use of monorails or floor tracks.
The control process involves:
- Software – considered the simplest method and suitable for manipulator robots.
- Adaptive control – these robots are equipped with sensory sensors, the main function of which is to independently determine and analyze the process of task execution and make decisions about further actions.
- Artificial intelligence.
- Remote human control.
Industrial robots find extensive applications in various sectors. The main categories include:
- Welding robots
- Machine-building robots
- Cutting robots
- Picking robots
- Assembly robots
- Packaging robots
- Warehouse robots
- Painting robots.
For a deeper dive into the fascinating realm of robotics, explore the latest insights and information on our website at https://robotxworld.com/. Uncover the cutting-edge advancements, diverse applications, and transformative technologies shaping the world of robots. Join us on a journey through innovation and discovery as we navigate the intricate landscape of robotic technologies, unveiling the future of automation and artificial intelligence. Visit us today to stay informed and engaged with the evolving world of robotics.
Types
Next, let's consider the main types of industrial robots and the principles of their operation.
Specialized Robots industrial robots are used in palletizing, welding, and painting. Let's discuss each in more detail.
Painting Operations Painting parts of any type using an industrial robot always yields the desired and high-quality result. With proper programming, the material is applied evenly, without drips and streaks. Also, thanks to robotic painting, the risk of poisoning the body with harmful paint fumes is eliminated.
Welding Operations
Welding operations carried out by specialized robots significantly save time and labor costs. They are capable of creating structures ranging from the simplest to the most complex. Welding robots can be divided into the following categories:
-
Laser Welding
Thanks to laser welding, metal is not subject to deformation, and the welding process itself occurs at high speeds with minimal expenses. -
Arc Welding
During welding operations, an electric arc is formed, melting the material and filling the joint with it. Welding electrodes can be consumable or non-consumable. -
Spot Welding
This is the most common type of welding used in the processing of most metallic products. -
Gas Welding
The advantage of this type of welding is the rapid fusion of material through continuous gas supply to the torch. The generated flame reaches temperatures of 2,500–3,000 degrees. -
Plasma Welding
This technology is applied for welding complex metallic joints. Compressed ionized gas is used in the process, passing through the copper nozzle of the industrial robot.
Palletizing
A palletizing robot is capable of both loading goods onto pallets and unloading them for further transportation. The palletizing robot can handle loads ranging from a few kilograms to tons. It can operate around the clock, sorting any product through programming.
For reference, palletizing is the process of placing items on transportable pallets within the logistics cycle.
Manipulator Robots
A typical manipulator robot consists of 7 segments:
- Feedback sensor
- Gripper device
- Manipulator hand
- Manipulator arm
- Column
- Load-bearing structure
- Arm drive
Thanks to the coordinated operation of all segments, the robot's movements are smooth and precise.
Traditional Manipulator Robots
Such robots can perform complex manipulations at various angles. For moving parts, these robots may use special grippers or pneumatic suction cups.
Delta Robots
These robots are commonly used in the food, pharmaceutical, and electronic industries. Delta robots work on conveyor belts, precisely and rapidly arranging small parts.
SCARA Robots
For reference, SCARA stands for Selective Compliance Articulated Robot Arm, a kinematic system based on a lever mechanism. The rotational lever mechanism allows movement of the end effector in a plane.
SCARA robots are indispensable workers in confined spaces. These automated devices are particularly advantageous for assembling components that insert one part into another and do not require joining. An essential function of the robot is its ability to straighten and bend the working "elbow" in one plane, using minimal space.
Robots for Machine Tool Servicing
Such robots work collaboratively with machine tools, ensuring their continuous operation by loading materials around the clock. This increases the machine's productivity by 20%. The process unfolds as follows: the manipulator arm loads raw materials into the machine, and after processing, the robot extracts the finished part.
Note! One robot can service multiple machines simultaneously.
Collaborative Robots
Collaborative robots, or "cobots," work in collaboration with humans. Cobots are highly compact and safe for human interaction. They serve as excellent assistants, free from fatigue and loss of attention.
The main areas of application for cobots include the automotive and electronics manufacturing industries. Common operations involve loading, moving, and assembly.
Purposes and Applications
Industrial robots are most commonly employed in large factories and enterprises. Their main feature is the ability to operate 24/7 without human intervention, relying solely on a specialized program to control the robot.
Keep in mind. Industrial robots can be used to create a complete production cycle characterized by exceptional precision while reducing the risk of errors due to human factors.
Automotive Industry
The automotive industry is a leader in the integration of robots into the production cycle. This solution significantly reduces time and enhances safety in the manufacturing process.
The automotive sector consumes a third of all automated systems globally, acting as a primary driver in the development of industrial robotics.
Today, on any automotive assembly line or design studio, there are fewer humans and more robots. Future vehicles are almost entirely produced by robots: designing, welding, assembling, and even painting vehicles.
This approach improves profitability and makes the production process flexible, minimizing the risk of potential errors.
Electronics Manufacturing
The use of industrial manipulators in electronics manufacturing allows for process optimization. Industrial robots provide any company with the ability to automate production schedules and nearly eliminate manual tasks. Such manipulators quickly pay off due to a significant reduction in the cost of production.
Let's list the main advantages of using industrial robots in electronics manufacturing:
- Reduction of production injuries.
- High precision in task execution.
- Minimal human intervention in the production cycle.
- High quality of the finished product.
Food Industry
The use of robots in the food industry is gaining increasing popularity. Such automated mechanisms are applied in both primary and secondary food processing. Let's list the main areas of production where robots contribute effectively:
- Meat processing.
- Sorting fruits and vegetables.
- Cutting food products.
- Sorting of products.
- Decoration of confectionery products.
- Washing of food products.
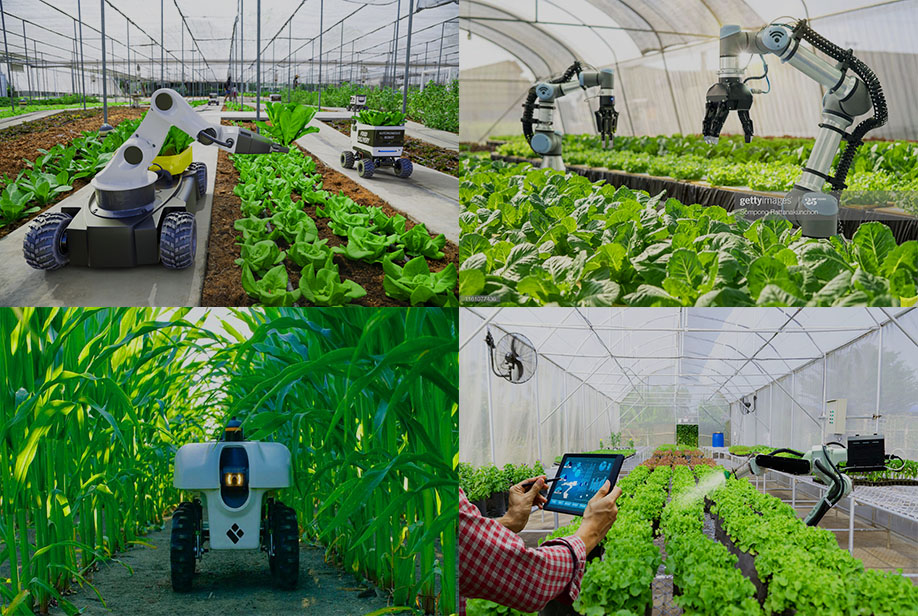

Agriculture
In agriculture, field robots are commonly used, and there are various categories of agricultural robots. Let's list them:
-
Drones (Unmanned Aerial Vehicles)
Used for crop monitoring, surveying fields, and assessing crop health from the air. -
Milking Robots
Automated systems for milking cows, enhancing efficiency and reducing manual labor. -
Manure Cleaning Robots
Robots designed to clean and manage animal waste, improving sanitation in agricultural facilities. -
Automatic Feed Distributors
Mechanisms that automate the distribution of feed to livestock, ensuring consistent and efficient feeding. -
Robotic Tractors and Harvesters
Autonomous or semi-autonomous tractors and combines that handle tasks such as plowing, planting, and harvesting.
The increasing costs of agricultural production, growing demand, and population expansion drive the widespread automation of agriculture. Today, robots assist in multiple tasks, including soil cultivation, fertilization, planting, livestock management, and animal feeding.
The use of such technology in agriculture yields positive results, namely:
-
Reducing the cost of production
Automation helps streamline operations, leading to cost savings in the long run. -
Improving quality indicators
Precision farming techniques contribute to better crop yields and product quality. -
Reducing environmental impact
Automation allows for more precise use of resources, minimizing environmental effects. -
Enhancing safety levels
Automated systems contribute to reducing the reliance on manual labor in potentially hazardous agricultural tasks, promoting safety in the industry.